
Digitalization is a process; it often takes place through a series of small, strategic improvements, with companies gradually adapting and optimizing their infrastructure. In this article, we present 7 essential elements for a successful smart factory that you can start implementing today.
The digital transformation toward smart factories is crucial for the future of the food industry. It offers vast opportunities to reduce costs and optimize processes, allowing for more flexible, transparent, and efficient operations. It also enables better responses to individual customer needs, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction. However, implementing a smart factory is not an overnight process. By starting small with technologies such as ERP systems, predictive planning tools, automation, and AI, companies can successfully progress towards a smart factory. Begin step by step, collaborate with experienced partners, and ensure that both technology and personnel are ready for future challenges. Here are the 7 indispensable technologies for achieving this goal.
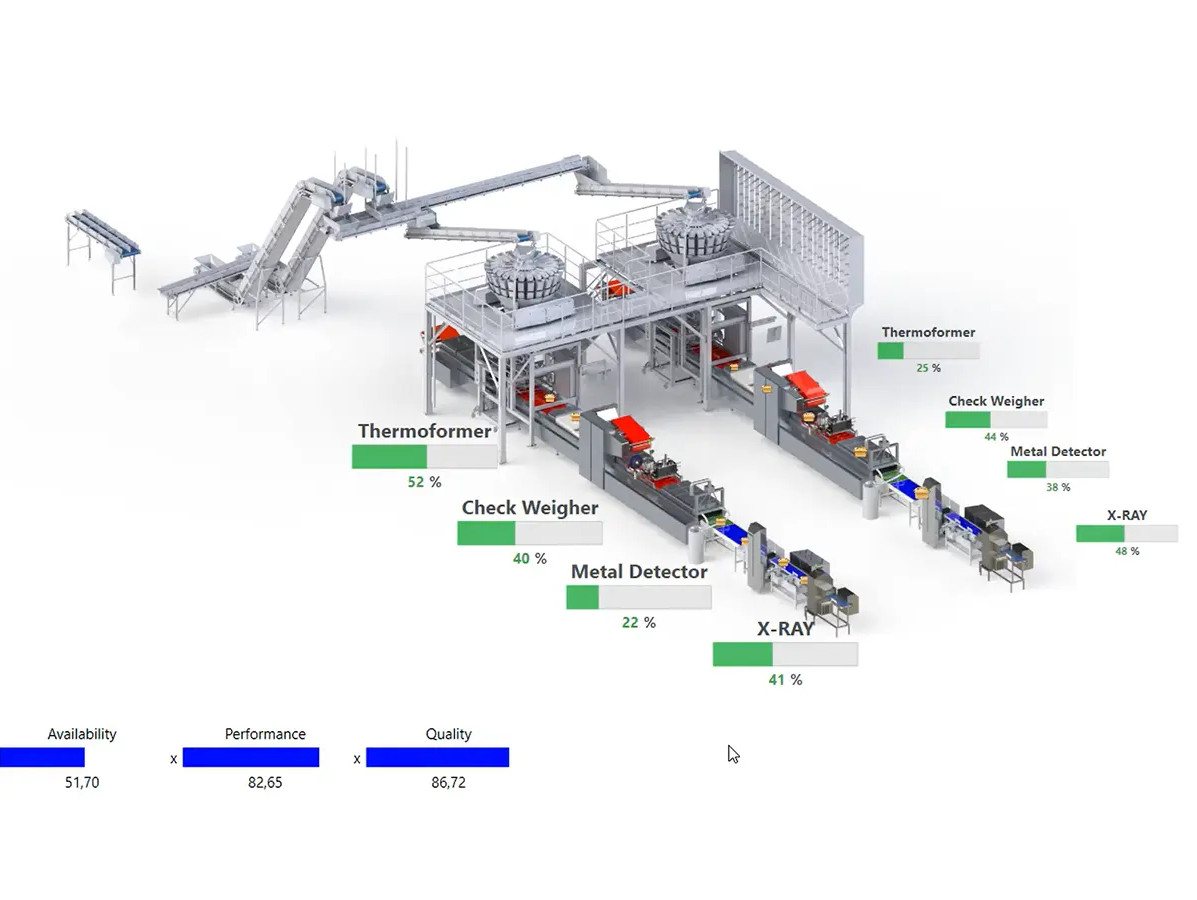
CSB-System Line Control (OEE)
The backbone of the smart factory
In a smart factory, machines, processes, and employees generate data continuously. However, this data is only valuable when it is quickly converted into actionable information. An ERP system plays a crucial role in this, acting as the central nervous system of the factory. Developed specifically for the food industry, these systems support not only traditional processes like cost management, recipe management, and sales and production planning, but also the integration and control of machines and systems. This results in an efficient flow of information from order to delivery. Thanks to ERP systems, food producers can operate faster and more effectively, which is critical in this competitive sector.
Flexible response to changing demand
The food industry is characterized by ever-changing demand from consumers and retailers. Predictive planning systems, integrated into the ERP system, take into account product variations, market fluctuations, and requirements such as same-day delivery. This allows for optimal planning of raw material purchases and sorting, minimizing setup times and avoiding bottlenecks. As a result, fluctuations in demand are processed immediately, and production plans are automatically optimized. Personalized orders and even small batches are handled efficiently, significantly reducing error margins.
More efficient production and logistics
Automation is one of the keys to success in the smart factory. It allows food producers to optimize individual processes or even entire production and logistics departments. Automation offers great advantages, particularly in intralogistics, such as automatic storage, sorting installations, and packaging lines. Combined with advanced IT and intelligent data management, these systems can autonomously handle increasingly complex processes. This improves efficiency, speeds up production, and reduces error rates in production processes.
Real-time monitoring for optimal efficiency
To achieve high levels of efficiency, the smart factory uses predictive maintenance and process optimization. This is made possible by sensors that continuously collect machine data. These systems record and analyze digital data from, for example, packaging machines, making correlations between faults and load immediately visible. This enables predictive maintenance, minimizing unplanned downtime and increasing productivity.
Smart automation and quality control
Industrial image processing is a powerful technology for improving the quality and efficiency of processes. This technology uses sensors and cameras to analyze data in real time and automate decisions, such as sorting raw materials or products. This leads to higher efficiency and accurate quality control. Thanks to AI, camera and image processing systems are becoming increasingly adept at performing better analyses, speeding up and enhancing the accuracy of processes like quality control.
Information available anywhere, anytime
In a smart factory, information is essential. Web- and cloud-based applications make it possible to connect all parts of the factory, from production to management. These apps generate real-time dashboards with important production data and performance indicators, accessible from any device. This gives managers and operators insight into performance, enabling them to make quick decisions.
Automated decision-making and optimization
AI is becoming increasingly important in the smart factory. It is already applied in various forms in all of the previously mentioned technologies. AI uses data to make intelligent decisions and optimize processes, such as predicting supply and demand, minimizing waste, and automating quality controls. One of the most valuable current applications is predictive maintenance, where AI systems learn from historical data to predict when a machine needs maintenance. This prevents unexpected downtime and increases productivity.
Source: Vakblad Voedingsindustrie 2024